Articles
Posted on August 8, 2025
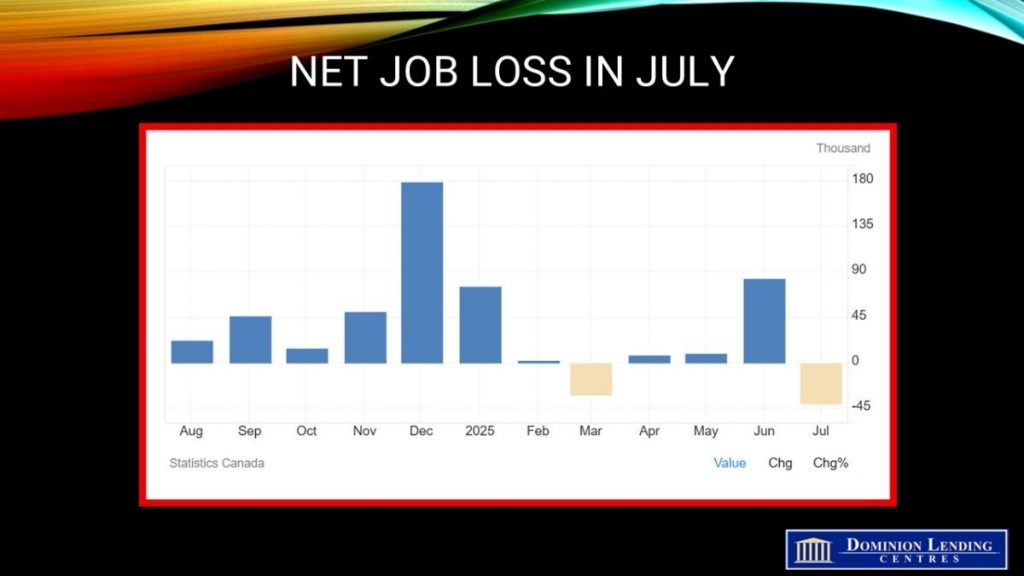
The July Labour Force Report showed a weaker-than-expected decline in net employment retracing some of June’s gain.
Canada’s July Labour Force Survey Was the Weakest Since 2022
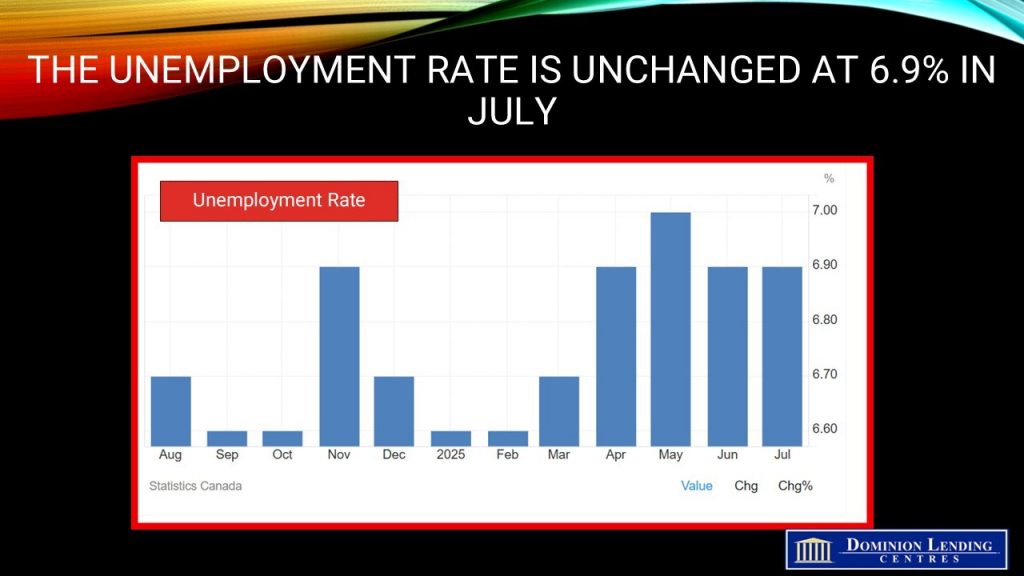
Employment fell by 40,800 jobs in July, a weak start to the third quarter, driven by decreases in full-time work, with most of the decline in the private sector. The jobless rate held steady at 6.9%, even though the number of unemployed people fell. The monthly decline was the largest since January 2022, and excluding the pandemic, it’s the most significant drop in seven years.
The job loss was concentrated among youth ages 15 to 24 who have had a terrible time finding summer jobs this year. The unemployment rate for that group is a whopping 14.6%, the highest since September 2010 outside of the pandemic. The youth employment rate fell 0.7 percentage points to 53.6% in July—the lowest rate since November 1998, excluding the pandemic.
Trump’s tariff turmoil has halted so many crucial financial decisions. Potential homebuyers are deer-in-the-headlights despite the relatively low mortgage rates, strong supply of unsold homes, and lower prices. Potential move-up buyers similarly don’t take action despite the relatively strong bargaining power of buyers.
The employment rate—the proportion of the population aged 15 years and older who are employed—fell by 0.2 percentage points to 60.7% in July and was down 0.4 percentage points from the beginning of the year (61.1% in both January and February).
The number of employees in the private sector fell by 39,000 (-0.3%) in July, partly offsetting a cumulative gain of 107,000 (+0.8%) in May and June. There was little change in the number of public sector employees and in the number of self-employed workers in July.
The unemployment rate held steady at 6.9% in July, as the number of people searching for work or on temporary layoff varied little from the previous month. The unemployment rate had trended up earlier in 2025, rising from 6.6% in February to a recent high of 7.0% in May, before declining 0.1 percentage points in June.
Unemployed people continued to face difficulties finding work in July. Of the 1.6 million people who were unemployed in July, 23.8% were in long-term unemployment, meaning they had been continuously searching for work for 27 weeks or more. This was the highest share of long-term unemployment since February 1998 (excluding 2020 and 2021).
Compared with a year earlier, unemployed job seekers were more likely to remain unemployed from one month to the next. Nearly two-thirds (64.2%) of those who were unemployed in June remained unemployed in July, higher than the corresponding proportion for the same months in 2024 (56.8%, not seasonally adjusted).
Despite continued uncertainty related to tariffs and trade, the layoff rate was virtually unchanged at 1.1% in June compared with a year ago (1.2%). This measures the proportion of people who were employed in June but were laid off in July. In comparison, the layoff rate for the corresponding months from 2017-19, before the pandemic, averaged 1.2%..
There were fewer people in the labour force in July as many discouraged workers dropped out, and the participation rate—the proportion of the population aged 15 and older who were employed or looking for work—fell by 0.2 percentage points to 65.2%. Despite the decrease in the month, the participation rate was little changed on a year-over-year basis.
Despite continued uncertainty related to tariffs and trade, the layoff rate was virtually unchanged at 1.1% in July compared with 12 months earlier (1.2%). This represents the proportion of people who were employed in June but had become unemployed in July as a result of a layoff. In comparison, the layoff rate for the corresponding months from 2017 to 2019, before the pandemic, averaged 1.2% (not seasonally adjusted).
There were fewer people in the labour force in July, and the participation rate—the proportion of the population aged 15 and older who were employed or looking for work—fell by 0.2 percentage points to 65.2%. Despite the decrease in the month, the participation rate was stable on a year-over-year basis.
Employment declined in information, culture and recreation by 29,000 (-3.3%). In construction, employment decreased by 22,000 (-1.3%) in July, following five consecutive months of little change. The number of people working in construction in July was about the same as it was 12 months earlier.
Employment fell in business, building and other support services (-19,000; -2.8%), marking the third decline in the past four months for the industry. Employment also fell in health care and social assistance (-17,000; -0.6%), offsetting a similar-sized increase in June. Compared with 12 months earlier, employment in health care and social assistance was up by 54,000 (+1.9%) in July.
Employment rose in transportation and warehousing (+26,000; +2.4%) in July, the first increase since January. On a year-over-year basis, employment in this industry was little changed in July.
The number of jobs declined in Alberta (-17,000; -0.6%) and British Columbia (-16,000; -0.5%), while it increased in Saskatchewan (+3,500; +0.6%). There was little change in the other provinces.
Total hours worked in July were little changed both in the month (-0.2%) and compared with 12 months earlier (+0.3%).
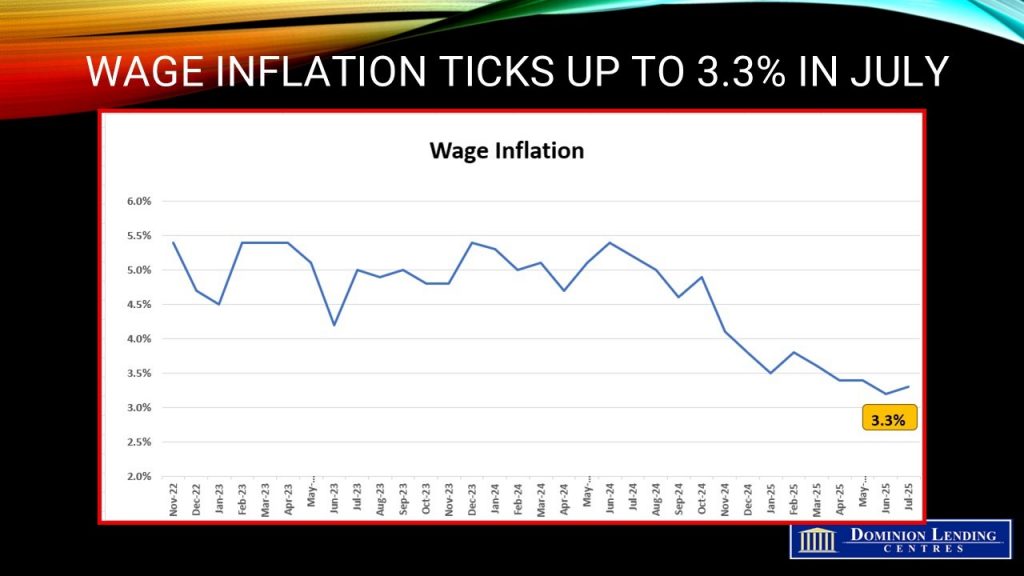
Average hourly wages among employees increased 3.3% (+$1.17 to $36.16) on a year-over-year basis in July, following growth of 3.2% in June (not seasonally adjusted).
Bottom Line
The two-year government of Canada bond yield fell about four bps on the news, while the loonie weakened. Traders in overnight swaps fully priced in a quarter-point rate cut by the Bank of Canada by year-end, and boosted the odds of a September cut to about 40%, from 30% previously.
Oddly enough, manufacturing payrolls rose in July despite the tariffs. This was the second consecutive monthly gain for a sector that one would expect to be most affected by the trade war. Manufacturing employment has fallen year-over-year.
This was an unambiguously weak report, but it comes hard on the heels of a robust report. Averaging the two months of data suggests there is an excess supply in the economy. But we will need to see a decline in core inflation for the Bank of Canada to resume cutting interest rates.
Traders are now expecting the US central bank to cut interest rates when it meets again in September. With any luck at all, this will pressure the Bank to cut rates as well, but only if the interim two inflation reports show an improvement, and the labour market remains weak. The next jobs report is on September 5, and the Bank of Canada meets again on September 17.
February 27, 2026
Canada’s Economy Declined by 0.6% in Q4, Taking Overall Real GDP Growth to 1.7% in 2025.
February 18, 2026
Canadian home sales fell 5.8% m/m in January, depressed by record winter storm in Ontario
February 6, 2026