Articles
Posted on August 19, 2025
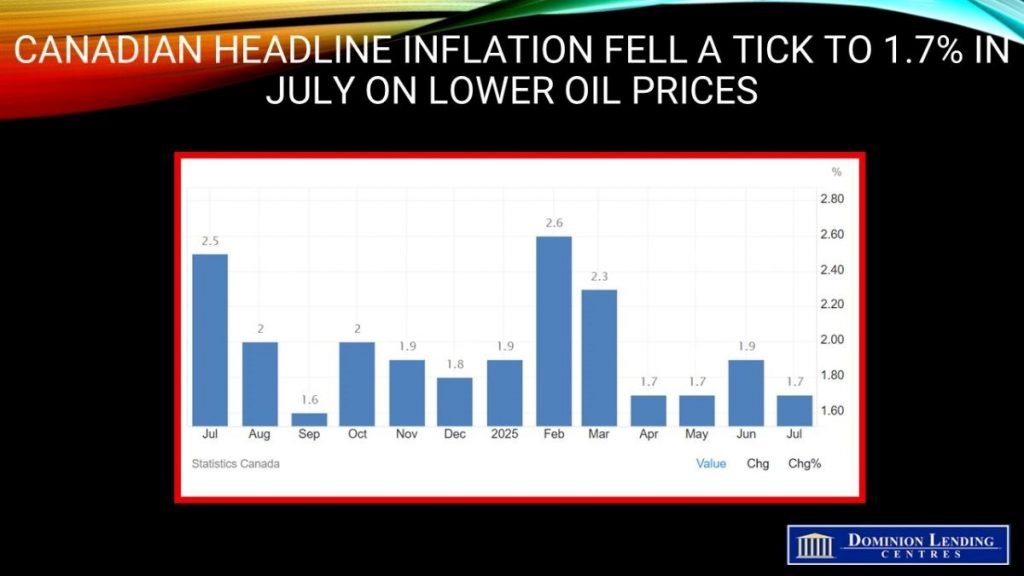
Canadian CPI Inflation Decelerated to 1.7% in July, from 1.9% in June mainly on lower oil prices.
Today’s CPI Report Shows Headline Inflation Cooling, But Core Inflation Remains Troubling
Canadian consumer prices decelerated to 1.7% y/y in July, a bit better than expected and down two ticks from June’s reading.
Gasoline prices led the slowdown in the all-items CPI, falling 16.1% year over year in July, following a 13.4% decline in June. Excluding gasoline, the CPI rose 2.5% in July, matching the increases in May and June.
Gasoline prices fell 0.7% m/m in July. Lower crude oil prices, following the ceasefire between Iran and Israel, contributed to the decline. In addition, increased supply from the Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries and its partners (OPEC+) put downward pressure on the index.
Moderating the deceleration in July were higher prices for groceries and a smaller year-over-year decline in natural gas prices compared with June.
The CPI rose 0.3% month over month in July. On a seasonally adjusted monthly basis, the CPI was up 0.1%.
In July, prices for shelter rose 3.0% year over year, following a 2.9% increase in June, with upward pressure mostly coming from the natural gas and rent indexes. This was the first acceleration in shelter prices since February 2024.
Prices for natural gas fell to a lesser extent in July (-7.3%) compared with June (-14.1%). The smaller decline was mainly due to higher prices in Ontario, which increased 1.8% in July after a 14.0% decline in June.
Rent prices rose at a faster pace year over year, up 5.1% in July following a 4.7% increase in June. Rent price growth accelerated the most in Prince Edward Island (+5.6%), Newfoundland and Labrador (+7.8%) and British Columbia (+4.8%). Moderating the acceleration in shelter was continued slower price growth in mortgage interest cost, which rose 4.8% year over year in July, after a 5.6% gain in June. The mortgage interest cost index has decelerated on a year-over-year basis since September 2023.
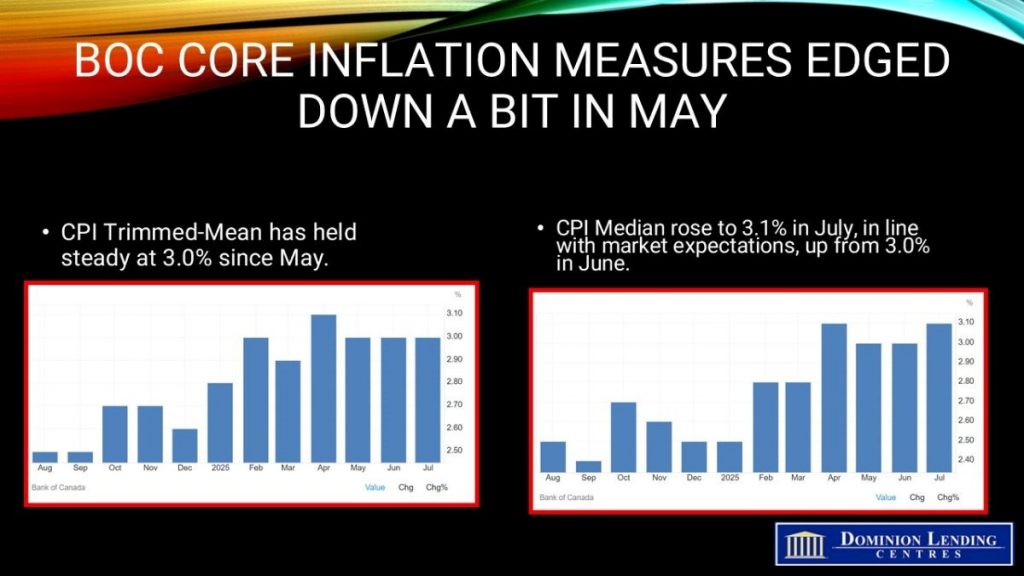
The Bank of Canada’s two preferred core inflation measures accelerated slightly, averaging 3.05%, up from 3% in May, and above economists’ median projection. Traders see the continued strength in core inflation as indicative of relatively robust household spending. There’s also another critical sign of firmer price pressures: The share of components in the consumer price index basket that are rising by 3% or more — another key metric the central bank’s policymakers are watching closely — expanded to 40%, from 39.1% in June.
CPI excluding taxes eased to 2.3%, while CPI excluding shelter slowed to 1.2%. CPI excluding food and energy dropped to 2.5%, and CPI excluding eight volatile components and indirect taxes fell to 2.6%.
The breadth of inflation is also rising. The share of components with the consumer price index basket that are increasing 3% and higher — another key metric that the bank’s policymakers are following closely — fell to 37.3%, from 39.1% in June.
Bottom Line
With today’s CPI painting a mixed picture, the following inflation report becomes more critical for the Governing Council. The August CPI will be released the day before the September 17 meeting of the central bank. There is also another employment report released on September 5.
Traders see roughly 84% odds of a Federal Reserve rate cut when they meet again on Sept 17–the same day as Canada. Currently, the odds of a rate cut by the BoC stand at 34%. Unless the August inflation report shows an improvement in core inflation, the Bank will remain on the sidelines.
February 27, 2026
Canada’s Economy Declined by 0.6% in Q4, Taking Overall Real GDP Growth to 1.7% in 2025.
February 18, 2026
Canadian home sales fell 5.8% m/m in January, depressed by record winter storm in Ontario
February 6, 2026