Articles
Posted on July 15, 2025
Canadian Inflation Accelerates by 1.9% y/y in June; US inflation comes in below forecast for the fifth consecutive month
Today’s Report Shows Inflation Remains a Concern, Forestalling BoC Action
Canadian consumer prices accelerated for the first time in four months in June, and underlying price pressures firmed, likely keeping the central bank from cutting interest rates later this month.
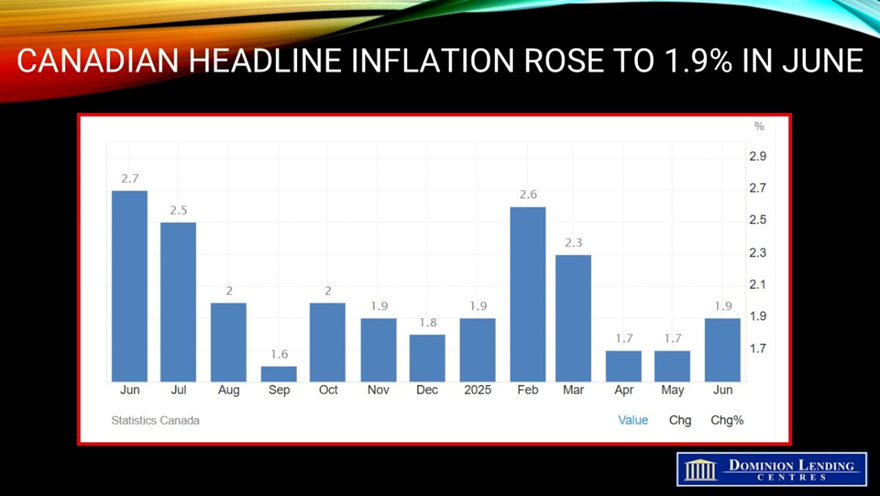
The annual inflation rate in Canada rose to 1.9% in June from 1.7% in May, aligning with market expectations. Despite the pickup, the rate remained below the Bank of Canada’s mid-point target of 2% for the third consecutive month.
Headline inflation grew at a faster pace, as gasoline prices fell to a lesser extent in June (-13.4%) than in May (-15.5%). Additionally, faster price growth for some durable goods, such as passenger vehicles and furniture, put upward pressure on the CPI in June.
Prices for food purchased from stores rose 2.8% year-over-year in June, following a 3.3% increase in May.
Year over year, the CPI excluding energy (+2.7%) remained higher than the CPI in June, partly due to the removal of consumer carbon pricing in April.
Monthly, the CPI rose 0.1% in June. On a seasonally adjusted monthly basis, the CPI was up 0.2%.
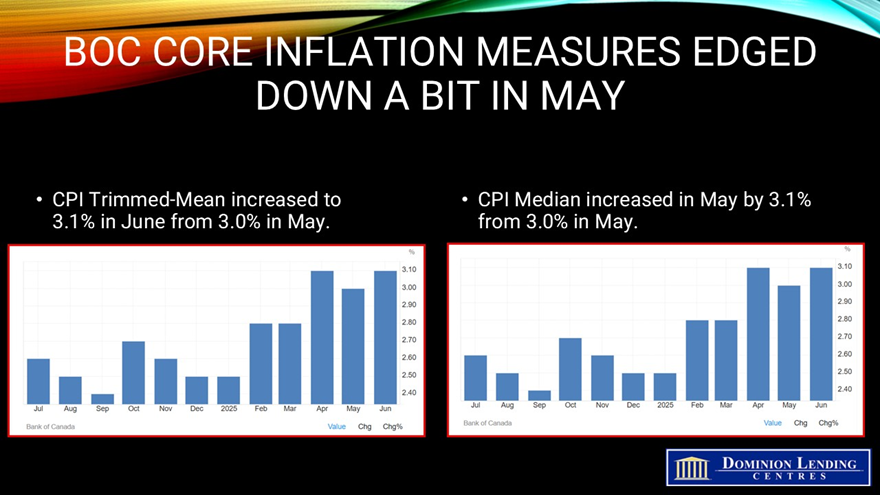
The Bank of Canada’s two preferred core inflation measures accelerated slightly, averaging 3.05%, up from 3% in May, and above economists’ median projection. The three-month moving annualized average of the core rates surged to 3.39%, from 3.01% previously.
There’s also another important sign of firmer price pressures: The share of components in the consumer price index basket that are rising by 3% or more — another key metric the central bank’s policymakers are watching closely — expanded to 39.1%, from 37.3% in May.
Bottom Line
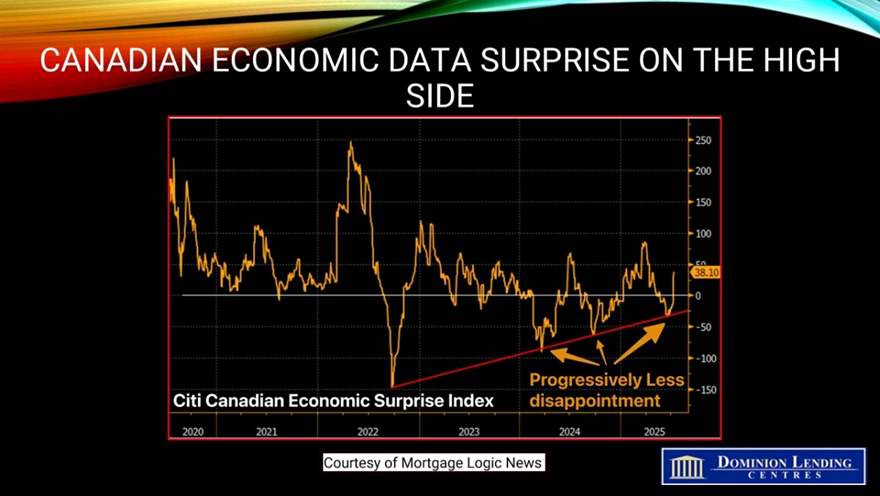
The chart below, created by our friends at Mortgage Logic News, shows that Canadian economic data have come in stronger than expected on average in recent weeks. This was evident in the June employment report. As a result, the Bank of Canada is likely to remain on the sidelines on July 30 for the third consecutive meeting. The Canadian economy appears to be weathering the tariff storm better than expected, at least for now.
While we expect to see a negative print on Q2 GDP growth, a bounce back to positive growth in Q3 is also possible, precluding the much-expected Canadian recession.
The June inflation data, released today for the US, was weaker than expected for the core price index. Declines in car prices helped mitigate tariff-related increases in other goods within the US consumer basket.
The US inflation data could draw even greater calls from President Trump for the Federal Reserve to lower interest rates. While some officials have expressed a willingness to cut rates when the central bank meets in two weeks, policymakers are generally still divided as to whether tariffs will cause a one-time price shock or something more persistent. They will leave rates unchanged for now.
February 27, 2026
Canada’s Economy Declined by 0.6% in Q4, Taking Overall Real GDP Growth to 1.7% in 2025.
February 18, 2026
Canadian home sales fell 5.8% m/m in January, depressed by record winter storm in Ontario
February 6, 2026