Articles
Posted on July 12, 2024
June Home Sales in Canada Show Early Signs Of A Pick-Up After BoC Easing
Early Signs Of Renewed Life In June Housing Markets
The Canadian Real Estate Association (CREA) announced today that national home sales rose 3.7% between May and June following the Bank of Canada’s rate cut. While activity was still muted, it wasn’t nearly as weak as the media recently portrayed.
“It wasn’t a ‘blow the doors off’ month by any means, but Canada’s housing numbers did perk up a bit on a month-over-month basis in June following the first Bank of Canada rate cut,” said Shaun Cathcart, CREA’s Senior Economist. “Year-over-year comparisons don’t look great mainly because of how many buyers were still jumping into the market last spring, but that’s a story about last year. What’s happening right now is that sales were up from May to June, market conditions tightened for the first time this year, and prices nationally ticked higher for the first time in 11 months”.

New Listings
The number of newly listed properties rose 1.5% last month, led by the Greater Toronto Area and British Columbia’s Lower Mainland. As of the end of June 2024, there were about 180,000 properties listed for sale on all Canadian MLS® Systems, up 26% from a year earlier but still below historical averages of around 200,000 for this time of the year.
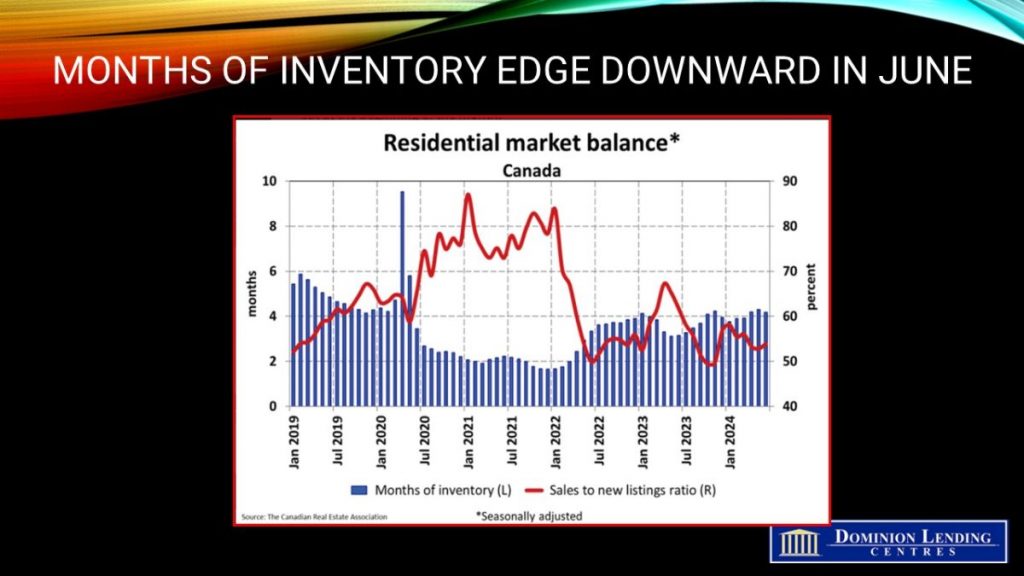
As the national increase in new listings was smaller than the sales gain in June, the national sales-to-new listings ratio tightened to 53.9% compared to 52.8% in May. The long-term average for the national sales-to-new listings ratio is 55%, with a sales-to-new listings ratio between 45% and 65%, generally consistent with balanced housing market conditions.
“The second half of 2024 is widely expected to see the beginnings of a slow and gradual return of buyers into the housing market,” said James Mabey, Chair of CREA. “Those buyers will face a considerably different shopping experience depending on where they are in Canada, from multiple offers in places like Calgary to the most inventory to choose from in over a decade in places like Toronto.
At the end of June 2024, there were 4.2 months of inventory nationwide, down from 4.3 months at the end of May. This was the first time that the number of months of inventory had fallen month over month in 2024. The long-term average is about five months of inventory.
Home Prices
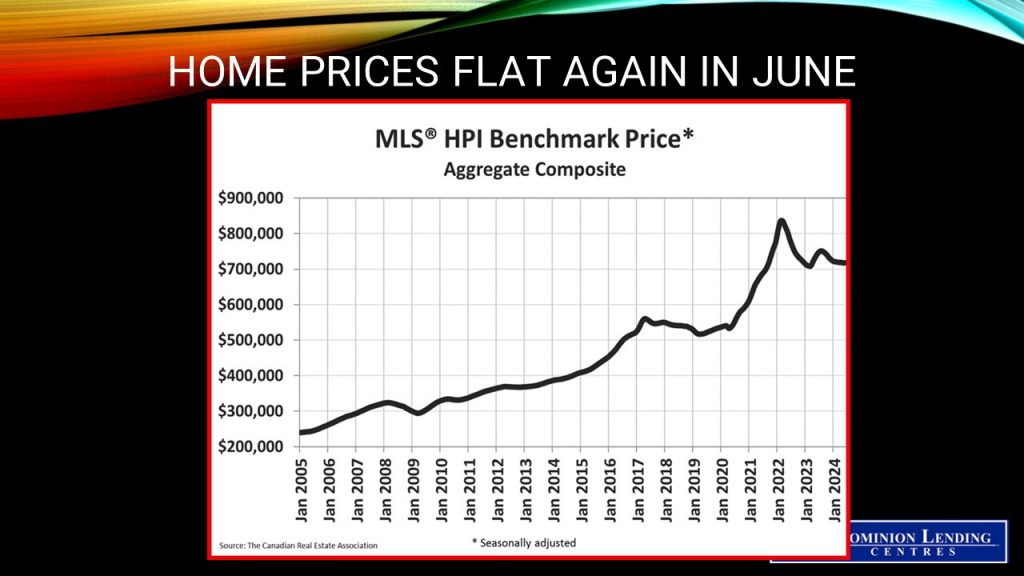
The National Composite MLS® Home Price Index (HPI) increased by 0.1% from May to June. While a slight increase, it was noteworthy because it was the first month-over-month gain in 11 months.
Regionally, prices are still generally sliding sideways across much of the country. The exceptions remain Calgary, Edmonton, and Saskatoon, and to a lesser extent Montreal and Quebec City, where prices have steadily increased since the beginning of last year.
That said, there have been more recent upward price movements in other markets, including across Ontario cottage country, Mississauga, Hamilton-Burlington, Kitchener-Waterloo, Cambridge, London-St. Thomas, and Halifax- Dartmouth.
The non-seasonally adjusted National Composite MLS® HPI stood 3.4% below June 2023. This mostly reflects how prices took off last April, May, June, and July – something that has not been repeated in 2024.
Bottom Line
Housing activity will gradually accelerate over the next year as interest rates continue to fall. Yesterday, bond yields fell considerably due to the marked improvement in the June US inflation data. Markets are now pricing in a 90% chance of a Federal Reserve rate cut in September, allaying fears that the Canadian dollar will decline precipitously if the Bank of Canada continues to go it alone in easing monetary conditions.
Next week’s CPI data will determine whether the Bank of Canada cuts rates at their July confab or waits until the September meeting. A further reduction in core inflation will open the doors to another rate cut on July 24, particularly given the continued rise in the Canadian unemployment rate. Rising monthly mortgage payments in the wake of record renewals will continue to slow discretionary consumer spending, providing further impetus for Bank of Canada rate cuts.