Articles
Posted on July 31, 2019
The Fed’s Quarter-Point Rate Cut Not the Start of Something Big
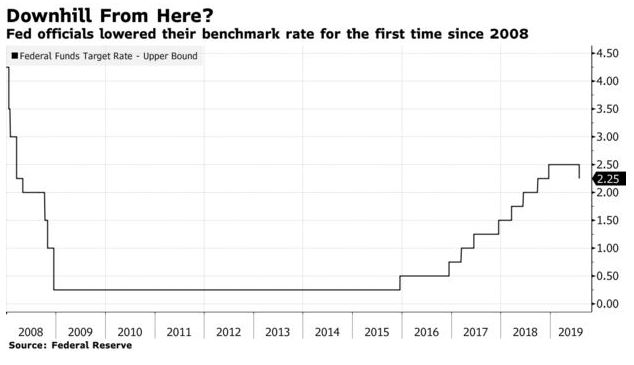
 The Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) cut the overnight target rate by 25 basis points as expected today. Chairman Jerome Powell, however, said it was designed to “insure against downside risks” rather than to signal the start of multiple rate cuts. President Trump called for “large” rate cuts on Twitter and has for months pressured the Fed to ease monetary policy. It is very unusual for the Fed to cut interest rates in the face of the continued strength in the US economy and the enormous declines in unemployment.
The Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) cut the overnight target rate by 25 basis points as expected today. Chairman Jerome Powell, however, said it was designed to “insure against downside risks” rather than to signal the start of multiple rate cuts. President Trump called for “large” rate cuts on Twitter and has for months pressured the Fed to ease monetary policy. It is very unusual for the Fed to cut interest rates in the face of the continued strength in the US economy and the enormous declines in unemployment.
I cannot remember a reversal of policy with so little impetus. Indeed, the opening sentences of the FOMC statement are, “Information received since the Federal Open Market Committee met in June indicates that the labor market remains strong and that economic activity has been rising at a moderate rate. Job gains have been solid, on average, in recent months, and the unemployment rate has remained low.”
The White House pressure is without precedent to the point that Trump publically threatened to demote Chairman Powell if the Fed didn’t cut rates. He also proposes to fill vacant seats with known rate doves. This infringement on Fed independence is very dangerous for the credibility of the central bank. Moreover, it will likely weaken the US dollar if additional rate cuts follow quickly.
Consumer spending remains strong; however, a slowdown in business fixed investment was caused by the President’s insistence on generating trade tensions with China, Canada, the UK and other trading partners. The global economy has slowed because of this uncertainty. China’s economy has decelerated significantly, and manufacturing and agricultural exports to China have been particularly hard hit.
Another issue of concern to the FOMC was the low level of inflation. The Fed targets a 2% inflation rate. The Fed’s favourite inflation measure is now running at about 1.4%-to-1.6%.
Two Federal Reserve Bank governors voted against this action preferring at this meeting to maintain the prior target range. It was the first time since Powell took over as chairman in February 2018 that two policymakers dissented.
Today’s action was the first interest rate cut since the financial crisis began more than a decade ago. The Fed started to normalize interest rates from historically low levels in 2015 as the US economy was recovering and continued to raise the fed funds rate until December 2018. Normalization of monetary policy also included the gradual shrinking of the Fed’s balance sheet–selling bonds into the marketplace, slowly reducing liquidity. Today, the Fed stated it would cease this activity as of tomorrow, rather than the planned date in September.
Bottom Line: The Bank of Canada will not follow the Fed. Canadian interest rates are already below those in the US. While the target range for the US fed funds rate is now 2%-to-2.25%, the target overnight rate in Canada is 1.75%. Moreover, today’s real GDP report for May surprised on the high side, suggesting that GDP growth in the second quarter could be close to 3%. This is well above the Bank’s earlier estimate and justifies the Bank’s remaining on the sidelines.