Articles
Posted on October 29, 2025
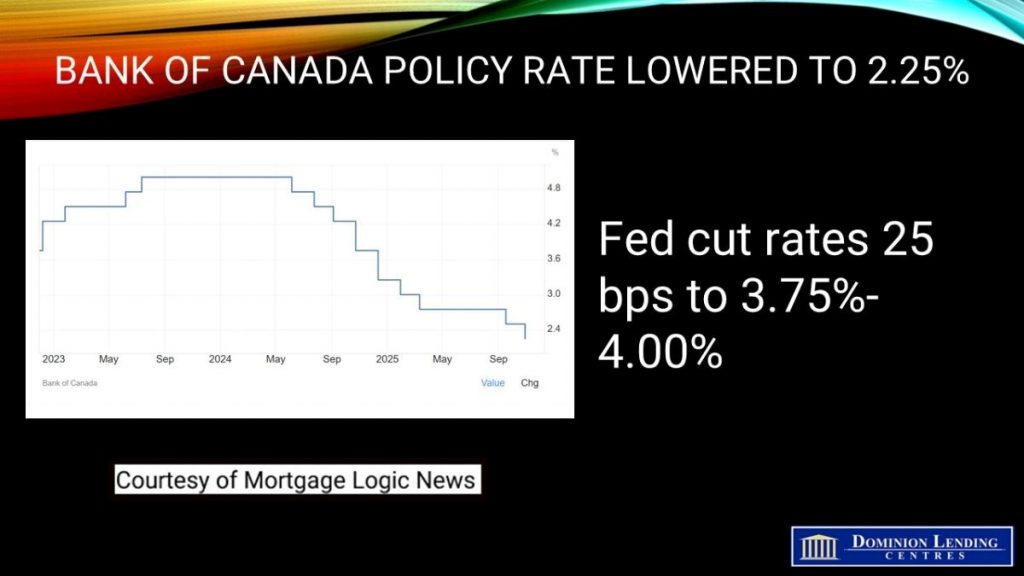
Bank of Canada Cuts Overnight Rate by 25 bps to 2.25%.
Bank of Canada Lowers Policy Rate to 2.25%
Today, the Bank of Canada lowered the overnight policy rate by 25 bps to 2.25% as was widely expected. This is the bottom of the Bank’s estimate of the neutral overnight rate, where monetary policy is neither expansionary nor contractionary. The economy will grow at about a 0.5% pace in Q3, causing the Bank to cut rates again at the final meeting this year on December 10. The easing will then end, but rates will remain relatively subdued until more trade uncertainty is alleviated.
The Fed is widely expected to cut rates by 25 bps this afternoon as well.
Today’s Monetary Policy Report suggests that the significant decline in export growth will persist for some time. Layoffs in trade-dependent sectors have already slowed considerably, especially in Ontario, Quebec, and some softwood lumber businesses in several provinces. The central bank acknowledged that “because US trade policy remains unpredictable and uncertainty is still higher than usual, this projection is subject to a wider-than-normal range of risks.”
“In the United States, economic activity has been strong, supported by the boom in AI investment. At the same time, employment growth has slowed and tariffs have started to push up consumer prices. Growth in the euro area is decelerating due to weaker exports and slowing domestic demand. In China, lower exports to the United States have been offset by higher exports to other countries, but business investment has weakened. Global financial conditions have eased further since July and oil prices have been fairly stable. The Canadian dollar has depreciated slightly against the US dollar.”
“Canada’s economy contracted by 1.6% in the second quarter, reflecting a drop in exports and weak business investment amid heightened uncertainty. Meanwhile, household spending grew at a healthy pace. US trade actions and related uncertainty are having severe effects on targeted sectors, including autos, steel, aluminum, and lumber. As a result, GDP growth is expected to be weak in the second half of the year. Growth will get some support from rising consumer and government spending and residential investment, and then pick up gradually as exports and business investment begin to recover.”
Canada’s labour market remains soft, and job vacancies have declined sharply despite the September improvement in job growth. Job losses continue to mount in trade-impacted sectors, and hiring has been weak across the economy. The unemployment rate remained at 7.1%, well above the US rate of 4.3%. Slower population growth translates into fewer new jobs and less inflation pressue. On a per capita basis, the economy is already in a recession.
The Bank projects GDP will grow by 1.2% in 2025, 1.1% in 2026 and 1.6% in 2027. Quarterly, growth strengthens in 2026 after a weak second half of this year. Excess capacity in the economy is expected to persist and be gradually absorbed.
“CPI inflation was 2.4% in September, slightly higher than the Bank had anticipated. Inflation excluding taxes was 2.9%. The Bank’s preferred measures of core inflation have been sticky around 3%. Expanding the range of indicators to include alternative measures of core inflation and the distribution of price changes among CPI components suggests underlying inflation remains around 2.5%. The Bank expects inflationary pressures to ease in the months ahead and CPI inflation to remain near 2% over the projection horizon”.
“If inflation and economic activity evolve broadly in line with the October projection, the Governing Council sees the current policy rate at about the right level to keep inflation close to 2% while helping the economy through this period of structural adjustment. If the outlook changes, we are prepared to respond. Governing Council will be assessing incoming data carefully relative to the Bank’s forecast.”
Bottom Line
The Bank of Canada has shown its willingness to bolster the Canadian economy amid unprecedented
trade uncertainty. While Canada is working hard to establish alternate trade partners, even China cannot replace the US in terms of proximity and cost-effectiveness, given the huge transport costs. China has stepped up its oil purchases to record levels, but larger oil flows east will require additional pipelines to BC. There is no market the size of the US market to replace exports of steel and aluminum. The US will also suffer from the economic impact of stepping away from the Canada-US-Mexico free trade deal. A renegotiation of the contract is likely to come before the end of next year. As of now, the US is signalling their desire to exit the agreement. We can only hope that cooler heads will prevail.
The auto industry is a case in point. Onshoring non-US auto production would require a 75% increase in US production and the construction of $50 billion in new factories. This would take years and significantly reduce the profitability of US auto companies.
Canada is the US’s number one supplier of steel and aluminum, with its competitively low hydroelectric costs. It will take time for the US to create the capacity to replace aluminum imports from Quebec.
Canada is the number one trading partner for 32 American states, many of which are lobbying Washington to end this CUSMA bashing.
It will take time for Canada to adjust to this new reality, which leads us to conclude that another cut in overnight rates is probable at the next decision date on December 10.